2016년 8월 20일 토요일
useful survey research.
1. tillion
: The Email rarely comes on time.
2. mypanel
: The Email rarely comes on time.
3. EMBRAIN
: The Email sometimes comes on time.
4. OpinionWorld
: The Email often comes on time.
5. mysurvey
: The Email sometimes comes on time.
6. panelnow
: The Email rarely comes on time.
7. Toluna
: The Email rarely comes on time.
8. ValuedOpinions
: The Email sometimes comes on time.
9. NETPOINT
: The Email rarely comes on time.
10. myvoicekorea
: The Email rarely comes on time.
11. SeoulGlobal
: The Email rarely comes on time.
12. iPanelonline
: The Email sometimes comes on time.
2016년 3월 29일 화요일
프린터 설치 (KONICA MINOLTA)
2. 프린터 및 팩스
오른쪽 마우스 -> 프린터 추가
네트워크, 무선 또는 Bluetooth 프린터 추가
사용가능한 프린터 찾는 중 후,
C364Series 선택
(프린터에 랜이 연결이 되어 있어야 함. 프린터 설명서의 IP 설정을 참조하셔도 되고).
여하튼 맞는 IP 선택. 만약 IP 선택을 잘못한다면?
큰 회사라면 자신의 문서가 다른 부서에서 인쇄될지도. ㅎㅎ~
아래의 글은 드라이버를 컴터에 다운 받았다고 가정하고 함.
프린터 추가 화면 뜸
디스크 있음 버튼 클릭
디스크에서 설치 화면 뜸
찾아보기 눌러.
D:\설치 프로그램\프린트 드라이버\코니카미놀타복합기드라이버\Drivers\PCL\KO\Win_x86
필자는 32bit 라 x86 선택
64bit 는 x64 폴더 선택
확인 버튼 눌름
KONICA MINOLTA C364Series 선택 후 다음 버튼 눌름
프린트 이름은 자기 마음대로
프린터 설치 중 화면 뜸
그냥 기다림
기본 프린터로 설정하든 말든 맘대로.
3. 네트웤 설정
4. 공유 폴더 설정
5. 프린터 수신지 등록
Scan to SMB 설정 방법
이상 끝~~
Today.
Life is a long lesson in humility. - James M. Barrie
(인생은 겸손에 대한 오랜 수업이다.)
2015년 3월 9일 월요일
Useful what(i)smy sites.
http://whatsmybrowsersize.com/
웹코딩을 하다가, 창 크기관련 스크립트가 잘 동작하지 않으면 위 사이트에 들어가보자.
브라우저 창의 크기를 마구 바꿔보자.
그리고 HTML 이나 스크립트 관련 사이트에 가서 다시 공부하자.
나는 천재가 아니기 때문에, 노력과 경험으로 커버해주마!!!
(While web coding, if the window size associated script does not work well let's go to the above site.
Let's harness change the size of the browser window.
Let's go back and learn HTML or script-related sites.
Since I am not a genius, I'll have to try and experience cover !!!)
http://www.whatismyip.com/
상단의 SPEED TEST 버튼도 클릭해보자.
(Let's also click on SPEED TEST button on the top.)
http://whatsmyuseragent.com/
웹을 공부하면 한번쯤 찾게 되는 사이트.
(When studying the websites found at least once.)
https://www.whatismybrowser.com/
desktop에서는 별로 사용할 필요가 없지만, 다른 기기(tablet, phone)에서는 필요한 사이트.
(Although you do not have to use much in the desktop, other devices (tablet, phone), the required site.)
2015년 2월 25일 수요일
Useful SQL queries
Date / Time related queries
-
Get the first day of the month
Quickly returns the first day of current month. Instead of current month you want to find first day of month where a date falls, replace SYSDATE with any date column/value.
SELECTTRUNC (SYSDATE,'MONTH')"First day of current month"FROMDUAL; -
Get the last day of the month
This query is similar to above but returns last day of current month. One thing worth noting is that it automatically takes care of leap year. So if you have 29 days in Feb, it will return 29/2. Also similar to above query replace SYSDATE with any other date column/value to find last day of that particular month.
SELECTTRUNC (LAST_DAY (SYSDATE))"Last day of current month"FROMDUAL; -
Get the first day of the Year
First day of year is always 1-Jan. This query can be use in stored procedure where you quickly want first day of year for some calculation.
SELECTTRUNC (SYSDATE,'YEAR')"Year First Day"FROMDUAL; -
Get the last day of the year
Similar to above query. Instead of first day this query returns last day of current year.
SELECTADD_MONTHS (TRUNC (SYSDATE,'YEAR'), 12) - 1"Year Last Day"FROMDUAL -
Get number of days in current month
Now this is useful. This query returns number of days in current month. You can change SYSDATE with any date/value to know number of days in that month.
SELECTCAST(TO_CHAR (LAST_DAY (SYSDATE),'dd')ASINT) number_of_daysFROMDUAL; -
Get number of days left in current month
Below query calculates number of days left in current month.
SELECTSYSDATE,LAST_DAY (SYSDATE)"Last",LAST_DAY (SYSDATE) - SYSDATE"Days left"FROMDUAL; -
Get number of days between two dates
Use this query to get difference between two dates in number of days.
SELECTROUND ( (MONTHS_BETWEEN ('01-Feb-2014','01-Mar-2012') * 30), 0)num_of_daysFROMDUAL;ORSELECTTRUNC(sysdate) - TRUNC(e.hire_date)FROMemployees;Use second query if you need to find number of days since some specific date. In this example number of days since any employee is hired.
-
Display each months start and end date upto last month of the year
This clever query displays start date and end date of each month in current year. You might want to use this for certain types of calculations.
SELECTADD_MONTHS (TRUNC (SYSDATE,'MONTH'), i) start_date,TRUNC (LAST_DAY (ADD_MONTHS (SYSDATE, i))) end_dateFROMXMLTABLE ('for $i in 0 to xs:int(D) return $i'PASSING XMLELEMENT (d,FLOOR (MONTHS_BETWEEN (ADD_MONTHS (TRUNC (SYSDATE,'YEAR') - 1, 12),SYSDATE)))COLUMNS iINTEGERPATH'.'); -
Get number of seconds passed since today (since 00:00 hr)
SELECT(SYSDATE - TRUNC (SYSDATE)) * 24 * 60 * 60 num_of_sec_since_morningFROMDUAL; -
Get number of seconds left today (till 23:59:59 hr)
SELECT(TRUNC (SYSDATE+1) - SYSDATE) * 24 * 60 * 60 num_of_sec_leftFROMDUAL;Data dictionary queries
-
Check if a table exists in the current database schema
A simple query that can be used to check if a table exists before you create it. This way you can make your create table script rerunnable. Just replace table_name with actual table you want to check. This query will check if table exists for current user (from where the query is executed).
SELECTtable_nameFROMuser_tablesWHEREtable_name ='TABLE_NAME'; -
Check if a column exists in a table
Simple query to check if a particular column exists in table. Useful when you tries to add new column in table using ALTER TABLE statement, you might wanna check if column already exists before adding one.
SELECTcolumn_nameASFOUNDFROMuser_tab_colsWHEREtable_name ='TABLE_NAME'ANDcolumn_name ='COLUMN_NAME'; -
Showing the table structure
This query gives you the DDL statement for any table. Notice we have pass ‘TABLE’ as first parameter. This query can be generalized to get DDL statement of any database object. For example to get DDL for a view just replace first argument with ‘VIEW’ and second with your view name and so.
SELECTDBMS_METADATA.get_ddl ('TABLE','TABLE_NAME','USER_NAME')FROMDUAL; -
Getting current schema
Yet another query to get current schema name.
SELECTSYS_CONTEXT ('userenv','current_schema')FROMDUAL; -
Changing current schema
Yet another query to change the current schema. Useful when your script is expected to run under certain user but is actually executed by other user. It is always safe to set the current user to what your script expects.
ALTERSESSIONSETCURRENT_SCHEMA = new_schema;Database administration queries
-
Database version information
Returns the Oracle database version.
SELECT*FROMv$version; -
Database default information
Some system default information.
SELECTusername,profile,default_tablespace,temporary_tablespaceFROMdba_users; -
Database Character Set information
Display the character set information of database.
SELECT*FROMnls_database_parameters; -
Get Oracle version
SELECTVALUEFROMv$system_parameterWHEREname='compatible'; -
Store data case sensitive but to index it case insensitive
Now this ones tricky. Sometime you might querying database on some value independent of case. In your query you might do UPPER(..) = UPPER(..) on both sides to make it case insensitive. Now in such cases, you might want to make your index case insensitive so that they don’t occupy more space. Feel free to experiment with this one.
CREATETABLEtab (col1 VARCHAR2 (10));CREATEINDEXidx1ONtab (UPPER(col1));ANALYZETABLEa COMPUTESTATISTICS; -
Resizing Tablespace without adding datafile
Yet another DDL query to resize table space.
ALTERDATABASEDATAFILE'/work/oradata/STARTST/STAR02D.dbf'resize 2000M; -
Checking autoextend on/off for Tablespaces
Query to check if autoextend is on or off for a given tablespace.
SELECTSUBSTR (file_name, 1, 50), AUTOEXTENSIBLEFROMdba_data_files;(OR)SELECTtablespace_name, AUTOEXTENSIBLEFROMdba_data_files; -
Adding datafile to a tablespace
Query to add datafile in a tablespace.
ALTERTABLESPACE data01ADDDATAFILE'/work/oradata/STARTST/data01.dbf'SIZE1000M AUTOEXTENDOFF; -
Increasing datafile size
Yet another query to increase the datafile size of a given datafile.
ALTERDATABASEDATAFILE'/u01/app/Test_data_01.dbf'RESIZE 2G; -
Find the Actual size of a Database
Gives the actual database size in GB.
SELECTSUM(bytes) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024ASGBFROMdba_data_files; -
Find the size occupied by Data in a Database or Database usage details
Gives the size occupied by data in this database.
SELECTSUM(bytes) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024ASGBFROMdba_segments; -
Find the size of the SCHEMA/USER
Give the size of user in MBs.
SELECTSUM(bytes / 1024 / 1024)"size"FROMdba_segmentsWHEREowner ='&owner'; -
Last SQL fired by the User on Database
This query will display last SQL query fired by each user in this database. Notice how this query display last SQL per each session.
SELECTS.USERNAME ||'('|| s.sid ||')-'|| s.osuser UNAME,s.program ||'-'|| s.terminal ||'('|| s.machine ||')'PROG,s.sid ||'/'|| s.serial# sid,s.status"Status",p.spid,sql_text sqltextFROMv$sqltext_with_newlines t, V$SESSION s, v$process pWHEREt.address = s.sql_addressANDp.addr = s.paddr(+)ANDt.hash_value = s.sql_hash_valueORDERBYs.sid, t.piece;Performance related queries
-
CPU usage of the USER
Displays CPU usage for each User. Useful to understand database load by user.
SELECTss.username, se.SID, VALUE / 100 cpu_usage_secondsFROMv$session ss, v$sesstat se, v$statname snWHEREse.STATISTIC# = sn.STATISTIC#ANDNAMELIKE'%CPU used by this session%'ANDse.SID = ss.SIDANDss.status ='ACTIVE'ANDss.usernameISNOTNULLORDERBYVALUEDESC; -
Long Query progress in database
Show the progress of long running queries.
SELECTa.sid,a.serial#,b.username,opname OPERATION,target OBJECT,TRUNC (elapsed_seconds, 5)"ET (s)",TO_CHAR (start_time,'HH24:MI:SS') start_time,ROUND ( (sofar / totalwork) * 100, 2)"COMPLETE (%)"FROMv$session_longops a, v$session bWHEREa.sid = b.sidANDb.usernameNOTIN('SYS','SYSTEM')ANDtotalwork > 0ORDERBYelapsed_seconds; -
Get current session id, process id, client process id?
This is for those who wants to do some voodoo magic using process ids and session ids.
SELECTb.sid,b.serial#,a.spid processid,b.process clientpidFROMv$process a, v$session bWHEREa.addr = b.paddrANDb.audsid = USERENV ('sessionid');- V$SESSION.SID AND V$SESSION.SERIAL# is database process id
- V$PROCESS.SPID is shadow process id on this database server
- V$SESSION.PROCESS is client PROCESS ID, ON windows it IS : separated THE FIRST # IS THE PROCESS ID ON THE client AND 2nd one IS THE THREAD id.
-
Last SQL Fired from particular Schema or Table:
SELECTCREATED,TIMESTAMP, last_ddl_timeFROMall_objectsWHEREOWNER ='MYSCHEMA'ANDOBJECT_TYPE ='TABLE'ANDOBJECT_NAME ='EMPLOYEE_TABLE'; -
Find Top 10 SQL by reads per execution
SELECT*FROM(SELECTROWNUM,SUBSTR (a.sql_text, 1, 200) sql_text,TRUNC (a.disk_reads / DECODE (a.executions, 0, 1, a.executions))reads_per_execution,a.buffer_gets,a.disk_reads,a.executions,a.sorts,a.addressFROMv$sqlarea aORDERBY3DESC)WHEREROWNUM < 10; -
Oracle SQL query over the view that shows actual Oracle connections.
SELECTosuser,username,machine,programFROMv$sessionORDERBYosuser; -
Oracle SQL query that show the opened connections group by the program that opens the connection.
SELECTprogram application,COUNT(program) Numero_SesionesFROMv$sessionGROUPBYprogramORDERBYNumero_SesionesDESC; -
Oracle SQL query that shows Oracle users connected and the sessions number for user
SELECTusername Usuario_Oracle,COUNT(username) Numero_SesionesFROMv$sessionGROUPBYusernameORDERBYNumero_SesionesDESC; -
Get number of objects per owner
SELECTowner,COUNT(owner) number_of_objectsFROMdba_objectsGROUPBYownerORDERBYnumber_of_objectsDESC;Utility / Math related queries
-
Convert number to words
More info: Converting number into words in Oracle
SELECTTO_CHAR (TO_DATE (1526,'j'),'jsp')FROMDUAL;Output:
one thousand five hundred twenty-six -
Find string in package source code
Below query will search for string ‘FOO_SOMETHING’ in all package source. This query comes handy when you want to find a particular procedure or function call from all the source code.
--search a string foo_something in package source codeSELECT*FROMdba_sourceWHEREUPPER(text)LIKE'%FOO_SOMETHING%'ANDowner ='USER_NAME'; -
Convert Comma Separated Values into Table
The query can come quite handy when you have comma separated data string that you need to convert into table so that you can use other SQL queries like IN or NOT IN. Here we are converting ‘AA,BB,CC,DD,EE,FF’ string to table containing AA, BB, CC etc. as each row. Once you have this table you can join it with other table to quickly do some useful stuffs.
WITHcsvAS(SELECT'AA,BB,CC,DD,EE,FF'AScsvdataFROMDUAL)SELECTREGEXP_SUBSTR (csv.csvdata,'[^,]+', 1,LEVEL) pivot_charFROMDUAL, csvCONNECTBYREGEXP_SUBSTR (csv.csvdata,'[^,]+', 1,LEVEL)ISNOTNULL; -
Find the last record from a table
This ones straight forward. Use this when your table does not have primary key or you cannot be sure if record having max primary key is the latest one.
SELECT*FROMemployeesWHEREROWIDIN(SELECTMAX(ROWID)FROMemployees);(OR)SELECT*FROMemployeesMINUSSELECT*FROMemployeesWHEREROWNUM < (SELECTCOUNT(*)FROMemployees); -
Row Data Multiplication in Oracle
This query use some tricky math functions to multiply values from each row. Read below article for more details.
More info: Row Data Multiplication In OracleWITHtblAS(SELECT-2 numFROMDUALUNIONSELECT-3 numFROMDUALUNIONSELECT-4 numFROMDUAL),sign_valAS(SELECTCASEMOD (COUNT(*), 2)WHEN0THEN1ELSE-1ENDvalFROMtblWHEREnum < 0)SELECTEXP (SUM(LN (ABS(num)))) * valFROMtbl, sign_valGROUPBYval; -
Generating Random Data In Oracle
You might want to generate some random data to quickly insert in table for testing. Below query help you do that. Read this article for more details.
More info: Random Data in OracleSELECTLEVELempl_id,MOD (ROWNUM, 50000) dept_id,TRUNC (DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE (1000, 500000), 2) salary,DECODE (ROUND (DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE (1, 2)), 1,'M', 2,'F') gender,TO_DATE (ROUND (DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE (1, 28))||'-'|| ROUND (DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE (1, 12))||'-'|| ROUND (DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE (1900, 2010)),'DD-MM-YYYY')dob,DBMS_RANDOM.STRING ('x', DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE (20, 50)) addressFROMDUALCONNECTBYLEVEL< 10000; -
Random number generator in Oracle
Plain old random number generator in Oracle. This ones generate a random number between 0 and 100. Change the multiplier to number that you want to set limit for.
--generate random number between 0 and 100SELECTROUND (DBMS_RANDOM.VALUE () * 100) + 1ASrandom_numFROMDUAL; -
Check if table contains any data
This one can be written in multiple ways. You can create count(*) on a table to know number of rows. But this query is more efficient given the fact that we are only interested in knowing if table has any data.
SELECT1FROMTABLE_NAMEWHEREROWNUM = 1;
If you have some cool query that can make life of other Oracle developers easy, do share in comment section.
2015년 2월 9일 월요일
Popular Shortcut Keys - Toad
| Hotkey | Function |
|---|---|
| F1 | Help |
| F2 | Toggle Full screen Editor |
| Shift+F2 | Toggle Full screen grid |
| F3 | Find Next Occurrence |
| Shift+F3 | Find Previous Occurrence |
| F4 | Describe Table,View,Procedure,Function,or Package in popup window |
| F5 | Editor: Execute as script |
| F6 | Toggle between Editor and Results panel |
| F7 | Clear All Text, Trace Into in the Editor |
| F8 | Recall previous SQL statement in the Editor, Step Over in the Editor for PL/SQL debugging |
| F9 | Execute statement in the SQL editor,Compile in the Editor |
| Ctrl+F9 | Verify statement without execution (parse) in the Editor, Set Parameters in the Editor for PL/SQL debugging |
| Shift+F9 | Execute current statement at cursor in the Editor, Execute Current Source in the Editor without PL/SQL debugging |
| F10 | Popup Menu |
| F11 | Run (continue execution) in the Procedure Editor for PL/SQL debugging |
| F12 | Run to cursor in the Editor for PL/SQL debugging. |
| Ctrl+F12 | Pass the SQL or Editor contents to the specified External Editor (Specified in Options Editors). |
| Ctrl+A | Select All Text |
| Ctrl+Alt+B | Display the PL/SQL Debugger Breakpoints window |
| Ctrl+C | Copy |
| Ctrl+D | Display procedure parameters |
| Ctrl+Alt+D | Display the PL/SQL Debugger DBMS Output window |
| Ctrl+E | Execute Explain Plan on the Current Statement |
| Ctrl+Alt+E | Display the PL/SQL Debugger Evaluate/Modify window |
| Ctrl+F | Find Text |
| Ctrl+G | Goto Line |
| Ctrl+L | Convert Text to Lowercase |
| Ctrl+M | Make Code Statement |
| Ctrl+N | Recall Named SQL Statement |
| Ctrl+O | Opens a Text File |
| Ctrl+P | Strip Code Statement |
| Ctrl+R | Find and Replace |
| Shift+Ctrl+R | Uses the ALIASES.TXT file to substitute the alias with the associated table name |
| Ctrl+S | Saves File |
| Shift+Ctrl+S | Save File As |
| Ctrl+Alt+S | Display the PL/SQL Debugger Call Stack window |
| Ctrl+T | Columns Dropdown |
| Ctrl+U | Converts Text to Uppercase |
| Ctrl+V | Paste |
| Ctrl+Alt W | Display the PL/SQL Debugger Watches window |
| Ctrl+X | Cut |
| Ctrl+Z | Undo Last Change |
| Shift+Ctrl+Z | Redo Last Undo |
| Alt+UP | Display Previous Statement |
| Alt+DOWN | Display Next Statement (after Alt UP) |
| Ctrl+HOME | In the data grids, goes to the top of the recordset |
| Ctrl+END | In the data grids, goes to the end of the recordset |
| Ctrl+TAB | Cycles through the collection of MDI Child windows |
| Ctrl+ENTER | Execute current SQL (same as Shift+F9) |
| Ctrl+. (Ctrl+period) | Autocompletes tablenames |
2014년 11월 20일 목요일
차변과 대변
가끔씩 내 전공분야가 아닌 다른 분야의 용어나 흐름을 듣을 때가 있다.
이때는 대부분 아~ 이런거구나 하면서 넘어간다.
내가 할 일은 오류가 없고 데이터의 정확성이 보장되는 프로그램을 만들고 유지하는 일이니깐.
그런데 역시 수박 겉 핥기 식은 한계가 있는 법이라. :)
용어의 뜻을 알아야 할때가 있다.
그래서 용어의 뜻을 물어보면 대부분의 회사 사람들이 다음과 같이 대답해준다.
"인터넷 찾아보면 나와."
...
그렇다. 대한민국은 인터넷 강국이기에 늘 이런 식이다.
그래서 인터넷을 찾아보았다.
차변은 거래의 분개시 왼쪽에 나타나는 거래로서 "자산의 증가,부채의감소,자본의감소,비용의발생"등을 왼쪽에 기입.
대변은 거래의 분개시 오른쪽에 나타나는 거래로서 차변의 반대적인 개념의 "자산의감소,부채의증가,자본의증가,수익의발생"등을 오른쪽에 기입
회계를 공부한 사람은 차대변에 대해서 잘 알 것이다.
하지만 나같은 사람은 잘 모른다.
그리고 인터넷에 나온 설명은 나에게 있어 '이건 뭐냐? 그래서 뭔데?' 정도이다.
그래서 내가 아는 정도는 최대한 찾아서 여기에 기록해 놓으려고 한다.
혹시 미래에 다른 누가 차대변에 대해 나에게 물어본다면 난 이 페이지를 보여주면서.
이게 내가 아는 차대변이다. 이게 내 실력의 한계일세 쏘리~
부끄럽지만 허허허. 라고...
자산.
- 자산(資産)이란 경제적인 가치가 있는 재화를 말한다. 선진국으로 갈수록 자산 분배율이 돈, 부동산, 주식 등에 고르게 나타나는 경향이 있다.
- 자산 = 자본(자본금 + 잉여금) + 부채
- 자산은 손익계산에 관한 회계학적 개념으로 수익에 대한 것을 의미하며 비용으로서 소비되고 수익에 의하여 회수된다. 따라서 자산은 소비되었으나(즉 현실적 이용성이 없으나), 아직 수익으로 전화되지 않고 비용으로서 유보되어 있는 것, 즉 차기 이후에 수익으로 전화할 것도 역시 가치가 인정되어 자산의 개념에 포함된다.
부채 (경제)
- 부채(負債)는 타인에게서 빚을 진 것을 말한다.
자본
- 경제학에서, 자본(資本)은 매우 다양한 의미로 쓰이는 개념이다. 일반적으로는 축적된 부 즉 많은 양의 화폐나, 토지·공장과 같이 생산의 밑거름이 되는 생산 수단을 말한다. 또, 자본은 돈(인간의 노동을 구매할 수 있는 권한)을 더 많이 획득하고자 할 때 사용되는 부(인간의 노동을 구매할 수 있는 권한이 축적되어 있는 상태)를 말한다. 경제학 상의 자본에는 기본자본 · 부가자본(기본자본과 부가자본을 합하여 자기자본이라 함) 및 외래자본(타인자본)이 있는데, 이 중에서 법률(상법)상의 자본금에 해당하는 개념은 자기자본만이다. 경제상의 개념인 부가자본은 대한민국 상법에서 준비금으로 규정하고 있으며(대한민국 상법 458조~461조), 외래자본 중 장기차입금의 일부는 상법에서 사채(社債)로 규정하고 있다(상 469조~516조의10).
잉여금
[경제] 기업 회계상 주식회사의 자기 자본 중에서 자본금을 초과하는 금액. 적립금, 준비금, 이월 이익금 따위를 통틀어 이르는 말로, 이익 잉여금과 자본 잉여금으로 나눈다.
자본잉여금은 주식발행자금 등에 의해, 이익잉여금은 이익의 발생 등에 의해, 재평가잉여금은 자산재평가의 평가익 등에 의해 발생한다.
* 여기까지 하다가 도저히 이해가 안되서 찾아본 사이트
<나는 이해가 안됨. 하지만 다른 사람들은 이해할 꺼임>
나는 머리가 나빠서...
비용
비용(費用, expense)이란 일반적으로 어떤 일을 하는 데 드는 돈을 말하며, 전문적 의미로는 소비된 가치의 크기를 말한다.
수익
회계에서 수익(收益)은 주요 영업활동으로 인한 자본(순자산)의 증가액이다. 자본은 자산에서 부채를 뺀 것이므로, 수익이 발생했다는 것 또는 자본이 증가했다는 것은 자산이 증가하거나 부채가 감소했다는 것을 의미한다. 수익에서 비용을 차감한 잔액을 이익이라고 한다.
* 여기까지의 설명으로 내가 생각한 개념 요약.
차변은 나한테 들어오는 것이고 대변은 나에게서 나가는 것이다 라고 큰 틀을 잡고 시작
예1)
외상매입금 150,000원을 현금으로 지급하다.
(차변) 부채의 감소 (대변) 자산의 감소
:
우선 외상매입금을 현금으로 지급하였으니, "부채의 감소"가 나에게 들어온 것이다.
그리고 빚을 갚기 위해 현금을 지급했으니 내 돈이 나간 것이다. "자산의 감소"
예2)
단기대여금 100,000원과 그에 대한 이자 100원을 현금으로 회수하다.
(차변) 자산의 증가 (대변) 자산의 감소, 수익의 발생
현금으로 100,100원이 들어왔다. "자산의 증가"
아래 1,2번 글은 순전히 나의 생각임.
1. 돈이 나에게 들어왔으니 "자산의 감소" 는 나간 것이 된다.
2. 그리고 대여로 받던 이자 "수익의 발생"이 나간 것이 된다.
돈을 빌려줬기 때문에 자산이 감소하던 것이 다시 받았으니 "자산의 감소"가 나갔다인데...
자산 = 자본(자본금 + 잉여금) + 부채 의 공식과 상관이 있을텐데...이 글을 읽는 사람에게 보류하겠다.
2번 글은 순전히 그냥 나의 생각. 역시 이 글을 읽는 사람에게 보류.
이런 것도 모르시냐라고 하시는 분들은 누가 혹시 이런 문제로 고생한다면 모른다고 구박하지 마시고 가르쳐주세요. LOL
* 예 1,2번을 보면서 그래도 나는 아리송한 것을 멈출 수가 없었다.
그런데 어떤 사람들은 위의 글들을 보고 바로 이해했고 궁금증이 풀렸다고 한다.
아무래도 나는 이해력이 심하게 떨어지는가 보다.
그래서 더 쉬운 것을 찾기로 했다.
* 그래서 예를 들어 설명한 글을 찾아보았다.
1) 식대로 현금 5,000원을 지불하다.
우선 복식에서는 계정 두 가지를 생각해야 합니다. 식대는 '복리후생비'라는 계정에 해당되고, '현금' 이라는 계정으로 지급하였습니다. 처음 부기를 익히는 사람은 '현금'도 계정이야? 하고 말하시겠지만 현금은 가장 대표적인 계정 중 하나입니다. 보통예금, 정기예금, 받을어음, 지급어음 등도 모두 계정의 이름이랍니다.
이제 [복리후생비][현금] 두 가지 계정을 왼쪽과 오른쪽으로 구분할 때 먼저 현금을 생각하면 쉽습니다. 식대로 현금을 주었으니 '현금' 계정은 오른쪽(대변)입니다. 그렇다면 분개는...
(차) 복리후생비 5,000 / (대) 현금 5,000
2) 통장에서 10,000원을 현금으로 인출했다.
이 예제의 두 가지 계정은 '보통예금'과 '현금'입니다. 보통예금은 나갔으니 오른쪽(대변)이 될 것이고, 현금은 들어왔으니 왼쪽(차변)이 될 것입니다.
(차) 현금 10,000 / (대) 보통예금 10,000
3) 상품을 판매하고 30,000원을 현금으로 받다.
상품을 판매한 것은 계정상 '매출'에 해당됩니다. 그러므로 이 거래의 두 가지 계정은 [매출]과 [현금]이 될 것입니다. 쉬운 쪽 현금이 들어왔으므로 왼쪽(차변)에 적고 물건이 나갔으니 오른쪽(대변)에 기록합니다.
(차) 현금 30,000 / (대) 매출 30,000
4) 거래처에서 상품을 매입하고 20,000 원을 통장에서 이체지급했다.
판매할 상품을 구매하는 것은 계정상 '매입'에 해당됩니다. 그러므로 이 거래의 두 가지 계정은 [매입]과 [보통예금]이 될 것입니다. 쉬운 쪽 보통예금이 나갔으므로 오른쪽(대변)이 되고 상품은 들어왔으므로 왼쪽(차변)이 될 것입니다.
(차) 매입 20,000 / (대) 보통예금 20,000
5) 상품 4,000원에 부가세 400원을 합하여 4,400원에 판매하고 현금으로 받다.
마지막으로 2개 이상의 계정을 생각해 봅시다. 대부분의 매출에는 부가세가 포함됩니다. 단지 관행에 따라 부가세를 별도로 계산하는 곳도 있고 소매점 같은 경우 부가세 포함 가격으로 거래하는 경우가 많습니다. 그러나 부가세를 별도로 기록해 주면 분기마다 부가세 신고 시나 결산 시 계산을 하기가 무척 수월합니다.
매출 시의 부가세는 계정상 '부가세예수금'에 해당됩니다. 보통 '매출'과 같은 쪽에 따라다닙니다.
(차) 현금 4,400 / (대) 매출 4,000
부가세예수금 400
: 예를 들어서 설명한 글을 보니 실제로 차대변을 어떻게 사용하는지 이해가 되었다.
하지만 나에게 회계업무를 주면서 차대변으로 분개한 자료 만들어봐~ 라고 한다면?
난 조용한 구석을 찾아 주저앉아 울 것이다.
* 그래서 다시 더 쉬운 그림으로 된 것을 찾아보았다.
마지막 장의 거래의 8요소가 다소 이상한 느낌이 나지만.
노동부랑 한국산업인력공단에서 만든건데;;;
하여튼 내가 생각하고 찾아본 차변과 대변은 여기까지.
회계사랑 변호사같은 친구가 있으면 정말 좋겠다.
결론 : 나는 친구가 적다.
2014년 11월 19일 수요일
키보드 특수문자 용어
그리고 며칠 후, 술자리에서 사람들이랑 이것저것 이야기하다가 특수문자를 발음해야되는데 순간 멍~
참고로 "*" 이 녀석을 뭐라고 불렀던지 기억이 안났음.
LOL :)
그래서 여기다가 기록
특수기호
!- Exclamation Point (엑스클러메이션 포인트)
“ - Quotation Mark (쿼테이션 마크)
# - Crosshatch (크로스해치), Sharp(샵), Pound Sign(파운드 사인)
$ - Dollar Sign (달러사인)
% - Percent Sign (퍼센트사인)
@ - At Sign (앳 사인, 혹은 앳), Commercial At(커머셜 앳)
& - Ampersand (앰퍼샌드)
' - Apostrophe (어파스트로피)
` - Grave (그레이브)
* - Asterisk (애스터리스크)
- - Hyphen (하이픈), Dash (대시)
. - Period (피리어드), Full Stop (풀스탑)
/ - Slash (슬래시), Virgule (버귤)
\ - Back Slash (백슬래시)
- Won sign (원사인)
: - Colon (콜론)
; - Semicolon (세미콜론)
^ - Circumflex (서컴플렉스), Caret (캐럿)
{ - Left Brace (레프트 브레이스)
} - Right Brace (라이트 브레이스)
[ - Left Bracket (레프트 브래킷)
] - Right Bracket (라이트 브래킷)
( - Left Parenthesis (레프트 퍼렌씨시스)
) - Right Parenthesis (라이트 퍼렌씨시스)
| - Vertical Bar (버티컬바)
~ - Tilde (틸드)
= - Equal Sign (이퀄사인)
+ - Plus Sign (플러스사인)
- - Minus Sign (마이너스사인)
_ - Underscore (언더스코어), Underline (언더라인)
< - Less Than Sign (레스댄 사인), Left Angle Bracket(레프트 앵글브래킷)
> - Greater Than Sign (그레이터댄 사인), Right Angle Bracket (라이트 앵글브래킷)
그리스알파벳
Α/α(알파) Β/β(베타) Γ/γ(감마) Δ/δ(델타)
Ε/ε(엡실론) Ζ/ζ(제타) Η/η(에타) Θ/θ(쎄타)
Ι/ι(요타) Κ/κ(카파) Λ/λ(람다) Μ/μ(뮤) Ν/ν(뉴)
Ξ/ξ(크시) Ο/ο(오미크론) Π/π(피) Ρ/ρ(로우)
Σ/σ(씨그마) Τ/τ(타우) Υ/υ(윕실론) Φ/φ(휘)
Χ/χ(키 또는 카이) Ψ/ψ(프시) Ω/ω(오메가)
수학기호
σ : 소문자 시그마는 표준편차를 나타내는 기호
Σ : 대문자 시그마는 아래첨자와 위첨자를 기입하여 합에 관한 기호로 사용
i : 아이. 허수단위. 제곱해서 -1이 되는 수입니다.
√ - 제곱근 또는 루트라고 읽습니다
ㅠ - 파이 : 소문자 파이는 원주율을 나타내는 기호로 3.141592... 값을 가지며,
대문자 파이는 확률에서 중복순열을 나타내거나 위첨자 아래첨자와 함께 쓰는
경우 곱에 관한 기호가 됩니다
∫ - 인테그랄 : 적분기호
∬ - 중적분 기호로, 적분을 두번 하라는 것입니다
(주: 세개있으면 삼중적분, 가운데 똥그라미가 있으면 선적분기호 입니다.)
∴ - 따라서 또는 그러므로 (주: hence 혹은 therefore 라고 읽습니다. -수학에 자주 나옴)
∵ - 왜냐하면 (주: because라고 읽습니다.)
≒ - 약: 근사값을 쓸때 또는 양쪽 값이 거의 비슷할때 사용
dθ - 디쎄타 - 미분에서 사용되는 기호입니다.
≡ - 합동 또는 모듈로(mod)를 나타내는 기호
∈ - (왼쪽이 오른쪽의) 원소이다.
∋ - (오른쪽이 왼쪽의) 원소이다.
∀ - 임의의
∃ - 존재한다. exist.
적분기호 : ∫, ∬, ∮ (주: 차례로 적분, 중적분, 선적분입니다.)
미분기호 : ∂(편미분)
삼각함수 : sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec, cot, sinh, cosh, tanh, sech, cosech, coth,
각각의 함수에 역함수 기호(^-1)를 붙이면 arc삼각함수(=역삼각함수)가 된다.
기타 : ∞(무한대), !(팩토리얼,factorial)
결론 : 나는 오늘 바쁘다.
2014년 6월 26일 목요일
개발에 유용한 사이트 fiddle
Web Test : <Where are U?>
.net Test : <Where are U?>
이건 내가 봐야될 공부해야 될 Test(쉽게 말해서 모름) : <Where are U?>
점점 사용자 편의를 위해 기술은 발전해가고 있는데.
...
...
...
나는 그냥 시간이 흐르는 것을 보고만 있구나.
2014년 6월 23일 월요일
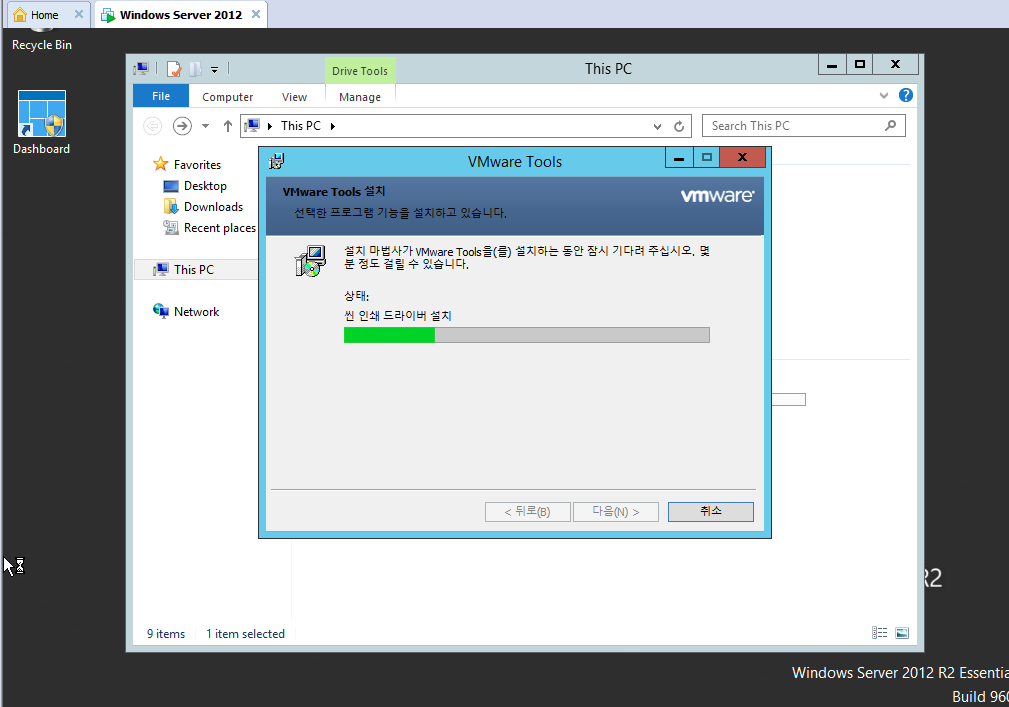
VMware Tools 설치해보자.
OS : Windows 8.1 K 64-bit (6.3, Build 9600)
Language : Korean
Processor : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3630QM CPU @ 2.40GHz (8 CPUs), ~2.4GHz
Memory : 8192MB RAM
Graphic : Intel(R) HD Graphics 4000
System Model : HP ENVY dv6 Notebook PC
VM: VMware Workstation 9.0.1
My mental state : not good
The reliability of this article : Low
설치 프로그램
Name : VMware Tools
Category : VMware option
Purpose : VMware 기능을 사용하려면 설치해야만 되서.
compatibility : ?
처음 VMware를 설치하면 로컬 PC에서 VM으로 파일이동이 안된다는 것을 알게된다.
물론 공유폴더라는 기능을 사용하면 되나.
ctrl + c, ctrl + v 라는 신공에 익숙한 나는 절대. never.
어케든 파일 복사 붙여넣기를 해야만 속이 시원하다.
그러므로 일단 해보자.
VM 메뉴에 보면 install VMware Tools... 라고 적혀있는게 있다.
그런데 너는 무슨 기능을 하는 애냐? <넌 누구냐?>
링크를 타고 들어가보면 알겠지만. 영어다.
일단 소중한 정보인 것을 대충이나마 짐작할 수 있을 것이다...
일단 D: 드라이브에 VMware Tools 항목이 들어가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
더블 클릭하면 창이 하나 뜨는데 당연히 Yes, Yes, Yes
설치는 컴터 몫.
나는 기다릴 뿐.
헐 기다려도 뭐 안되나 싶어서 그냥 멍하게 있었는데.
...
...
...
아래에 버젓이 이런 것이. 윽. 넌 날 모욕했어.
그냥 아무 일 없다는 듯이 설치 프로그램을 클릭하고 다음을 눌러주면 끝.
무조건 못 먹어도 다음.
go, go.
이제야 말로 그냥 멍하게 있으면 되겠군.
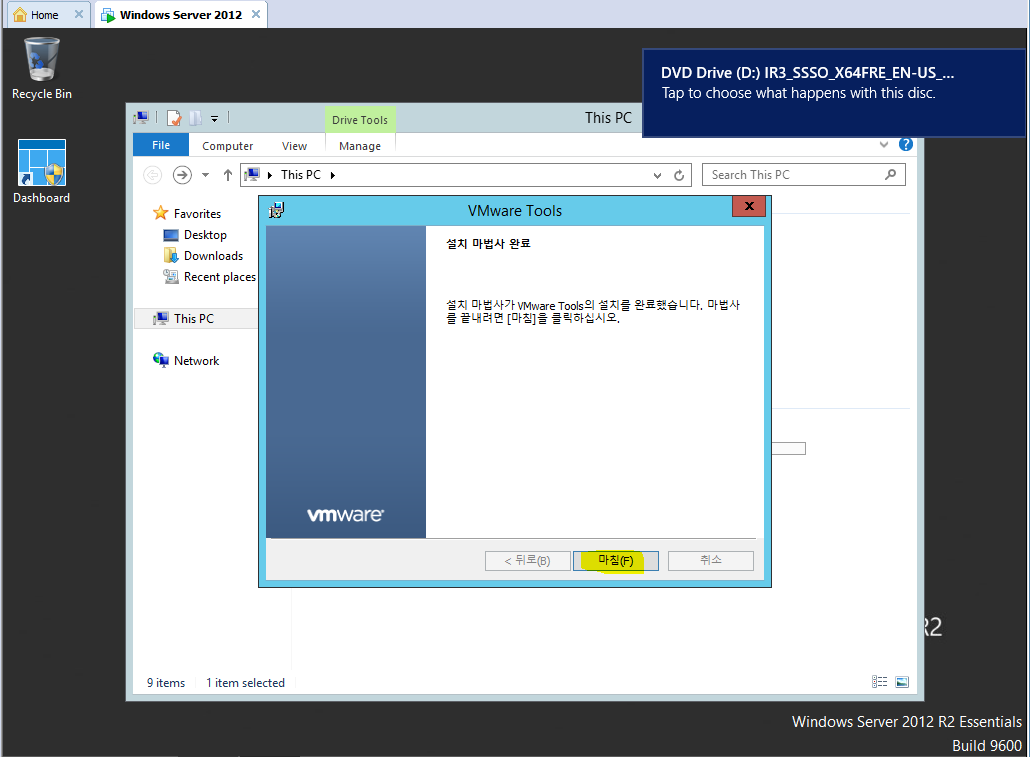
오 다 되었군.
너도 리부팅 좋아라 하는구나.
그래 열심히 리붓혀라. 어서~
오호, 리붓 하고 라니깐 이런게 생기네.
자, 그럼 내 로컬 PC에서 옮기고 싶은 파일 ctrl + c 를 해서.
VM 폴더에 ctrl + v 를.
...
...
...
오!!! 된다.
ㅎㅎㅎ 그런데 너 왜 복사 작업을 2번 하냐?
뭐 가상 머신이다 보니깐, 주소번지를 다시 재설정해줘야 되는 그런건가.
뭐 잘 되겠지.
오!!! 정말로 잘 되버렸다.
복사, 붙여넣기 신공이 완성되었으니 이제는 옮겨온 파일을 설치해봐야지.
아! 비온다. 비나 구경해야지.
2014년 6월 16일 월요일
VMware-workstation 설치
OS : Windows 8.1 K 64-bit (6.3, Build 9600)
Language : Korean
Processor : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3630QM CPU @ 2.40GHz (8 CPUs), ~2.4GHz
Memory : 8192MB RAM
Graphic : Intel(R) HD Graphics 4000
System Model : HP ENVY dv6 Notebook PC
My mental state : not good
The reliability of this article : Low
설치 프로그램
Name : VMware Workstation 9.0.1
Category : Virtual machines
Purpose : 일단은 DB 관련 내용을 몰아넣을 서버역할을 할 녀석이 필요해서 Hyper-V를 선택하였으나 (@_@' ㅋㅋ VT-d 라는 녀석땜시 포기하고 VMware 프로그램을 ㅎㅎ
compatibility : ?
우선 VMware Workstation 9.0.1 <넌 누구냐?>
아. 요즘같이 OS가 범람하는 시절에는 노아의 방주같은 배가 필요할 것같다.
몇년만 지나만 새로운 버전에 새로운 프로그램이 나오니깐. 휴~
그럼 노아의 방주같이 세상 동물들을 다 포함할 수 있는 프로그램은 무엇이냐?
답은 많다이다.
인터넷에 가상 머신이라고 치면 버츄얼박스, 버츄얼 머신, 하이퍼브이 등등 그것도 버전이 여러개다.ㅎㅎㅎ
결국 자신이 선택하면 된다.
그럼 난 VMware Workstation 9.0.1 을 선택했으니 이걸로 가보자.
우선 실행파일을 더블 클릭해서 실행하면.
늘 친숙한 Next 너늘 눌러주겠어.
나의 사전에 Cancel 은 없다.
아 물론 Active X같은 녀석은 무조건 Cancel이지만.
...
...
...
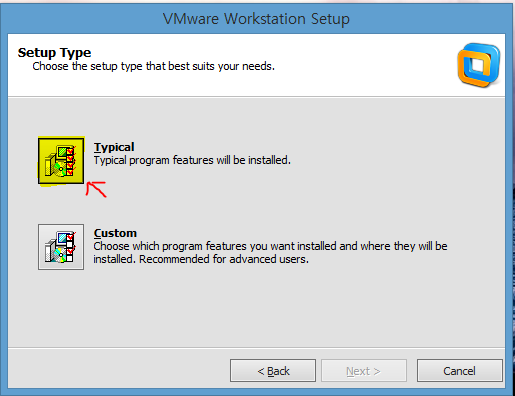
나에게 설치권을 물어봐야 난 멍해질 뿐이고,
그냥 Typical 이 최고지.
물론 다른 사람들은 Typical로 설치한다고 하더라도 우선 Custom에 들어가서 어떤 항목들이 설치되어지는지 확인하는 사람들이 있다.
확실히 확인을 하는것이 좋은 습관이라는 생각이 든다.
응응. 그렇지.좋은 행동이야.
하지만 역시 난 생각만 든다.
그리고 나도 모르게 이미 Typical을 누르고 말았지.
...
...
...
늘 친숙한 Next 너늘 눌러주겠어.
나의 사전에 Cancel 은 없다.
늘 친숙한 Next 너늘 눌러주겠어.
나의 사전에 Cancel 은 없다.
늘 친숙한 Next 너늘 눌러주겠어.
나의 사전에 Cancel 은 없다.
늘 친숙한 Next 너늘 눌러주겠어.
나의 사전에 Cancel 은 없다.
...
...
...
늘 친숙한 Next 너늘 눌러주겠어. -> Enter!!!
나의 사전에 Cancel 은 없다. -> Skip!!!
인터넷은 우주크기만큼 많은 자료가 있다. 찾아보자.
대망의 Finish.
설치된 폴더를 보면.
실행파일이 있네.
너를 실행시켜 보면.
그럼 이제 너를 설치했으니 담에는 진정한 가상머신의 능력을 보도록 하지.
대항해시대 조선 랭작
숙련도 획득 방법 선박 건조, 선박 강화, 전용함 추가시 숙련도 획득 모두 동일한 공식 적용 획득 숙련도 공식 기본 획득 숙련도 ≒ int{건조일수 × 현재랭크 × (0.525)} 이벤트 & 아이템 사용...
-
1. 장치 및 프린터 2. 프린터 및 팩스 오른쪽 마우스 -> 프린터 추가 네트워크, 무선 또는 Bluetooth 프린터 추가 사용가능한 프린터 찾는 중 후, C364Series 선택 (프린터에 랜이 연결이 되어 있어야 함. 프린터 ...
-
ERP 용어 용어 설명 ABAP/4 ( A dvanced B usiness A pplication P rogram for 4 -generation Language) 협업 비즈니스 솔루션 회사 SAP AG가 개발한 4세대 고급 프로그래밍...